Arthritis and osteoarthritis diseases that affect the joints. Cause pain during the movement, significantly reducing the quality of life. Arthritis and osteoarthritis what is the difference? In order to understand what arthritis is different from osteoarthritis it is necessary to know the common features, the peculiarities and the risk factors for each disease.
What happens in arthritis?
The disease developed inflammatory process that affects the entire body. The reasons for the development of the disease can be infection (infectious), trauma (traumatic), autoimmune diseases (rheumatoid arthritis).
Arthritis in the body is present in all signs of inflammation:
- The increase in body temperature, fever;
- The increase in the total blood proteins, immunoglobulins, C-reactive protein;
- May be accompanied by another inflammatory process, not previously identified.
What happens in osteoarthritis?
Osteoarthritis – a disease caused by the degradation of cartilage. The inflammatory process is localized only in the joint cavity, is a consequence of the deformation of the joint. The result is the increase of the voltage at the connection because of old age, after the injury, it can cause the deformation of the bone parts, the friction occurs between the surfaces of the joint. The result is a thinning and deformation of cartilage.
In this disease, the body no obvious signs of inflammation:
- The increase of the local temperature (only in the area of the affected joint);
- Biochemical and General blood tests is normal;
- Occurs when the deformation of cartilage, not accompanied by other inflammation.
The similarities and differences between the diseases.
The two diseases have both similarities and differences. The main similarity of the arthritis and osteoarthritis is the symptoms:
- Crack, crack on movement;
- Pain;
- The limitation;
- Swelling, redness in the affected joint.
However, the difference between arthritis and osteoarthritis more important than the similarities.
- Age. Arthritis – a disease that affects the elderly, the elderly. It is associated with age-related degradation of the cartilage of the joints. The arthritis often affects young people, is a consequence of the prolonged infection, inflammation in the body.
- The localization process. Osteoarthritis develops only in the joint under the action of risk factors (age, frequency, overload, excess weight, etc.). Arthritis affects the entire body, it can cause a rise in internal body temperature, fever.
- The pain. When arthritis pain in the extremities occurs during the movement acquires a permanent nature in the development of the disease. Arthritis there is a strong and constant pain.
- Deformity of the joint. In osteoarthritis of the bone connection components are deformed due to the degradation of cartilage. Arthritis does not cause changes in the articulating surfaces of the bones.
- Loss of motor function of the joints. The development of osteoarthritis leads to limiting the movement slowly. The arthritis restricts the movement only in the acute phase of the disease.
The difference in the causes of arthritis and osteoarthritis, the common causes.
In order to better understand the difference between the two diseases arthritis and osteoarthritis – it is necessary to know its causes.
Causes of arthritis are more likely to be:
- Infection (viruses, bacteria, fungi);
- Allergies, autoimmune diseases.
The main pre-conditions for the development of osteoarthritis:
- The overloading of the joint (activity, weight);
- Age-related degradation of cartilage.
In addition, there are a number of common causes for both diseases:
- Injury;
- Disorders of metabolic processes in the body.
- Insufficient intake of vitamins and minerals;
- Congenital disorders of the bone and cartilage.
The difference in the symptoms.
Signs of arthritis and osteoarthritis differ in character, severity, time of its appearance.
Symptoms |
Arthritis |
Osteoarthritis |
| 1. Increase of temperature | The body temperature increased to 38-39C | Perhaps the local increase of the temperature in the region of the affected joint |
| 2. Swelling | The soft tissues around the joint to be swollen of | Bumps appear on the 3rd stage of the disease |
| 3. The stiffness in the morning | Occurs all over the body | Occurs only in the affected connection |
| 4. The loss of motor functions | Only during the acute phase of the disease | Develops gradually, which leads to ankylosis (total absence of movement in the joint) |
| 5. To change the shape of the joint | Not happening | Happens |
| 6. The nature of the pain | Sharp, constant, worse at night | Insistent, boring, occurs when the movements are stronger in the morning. |
Due to the similarity of symptoms, the need arises in the differential diagnosis.
Diagnosis of diseases.
Proper and timely diagnosis helps to distinguish the arthritis from osteoarthritis and prescribe the most appropriate treatment. Basic methods of diagnosis in diseases of the joints, remain the same:
- The x-ray;
- Ultrasound of the joints;
- Biochemical analysis of blood;
- Arthroscopy.
Disease |
Diagnosis |
|||
Ultrasound |
X-ray |
A blood test |
Arthroscopy |
|
Osteoarthritis |
Reduction of the joint space, irregularities of cartilage. In the synovial fluid has contaminants. | Change the way anatomical of the joint, the presence of osteophytes (outgrowths of bone), the cartilage is thin, unequal. The interior of the joint space is reduced. | The absence of signs of inflammation – the main difference between osteoarthritis arthritis. | Osteophytes, the degradation of the cartilage, the reduction of the gap between the bone structures of the compounds. |
Arthritis |
Sinovialnye sheath of cartilage is uneven, the presence of inflammatory exudate in the joint cavity (pus). | Mild osteoporosis, a softening of bone tissue. | C-reactive protein, increased levels of alpha, beta-globulin, the appearance of antibodies in the blood, increased ESR. Increases the content of uric acid, in some cases there is anemia (decrease of hemoglobin). | The appearance of erosions in the cartilage and bone tissue, protrusion of the synovium into the joint cavity. |
Functions of treatment of arthritis and osteoarthritis.
Treatment of arthritis and osteoarthritis is a little different, which consists of:
- The pain and the inflammation.
- The maintenance of cartilaginous tissue of the joints.
- The recovery of the motor function of the joint.
- The prevention of relapses (repetitions).
The only difference in the treatment of arthritis is antibiotics, antiviral and antifungal medicines that are not prescribed for osteoarthritis. Doctors often prescribe penicillins, cephalosporins and aminoglycosides.

In the exacerbations of the disease and need treatment in the hospital.For the treatment of pain and inflammation are assigned non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (diclofenac, indomethacin). Ointments are appointed on the basis of these drugs (Fastum gel, voltaren, deep relief). In the absence of results of treatment of Nsaids can replace the injections of corticosteroid into the capsule connection.
Support of the cartilage of the joints to help the hyaluronic acid, hondroetina – hondroprotektory. To stop the degradation of joint tissue, stimulate the processes of regeneration. Courses their admission lasts from 1 to 10 months, depending on the stage of the disease.
The lack of results of conservative treatment and therapy can cause the goal of the operation. More often, a second arthroscopy, during which the cavity of the joint and remove inflammatory exudate, pieces of cartilage, blood clots. In the last stages of deformation units carried out the arthroplasty (joint replacement with artificial), osteotomy (resection of the deformed bone structures).
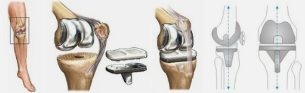
In addition, doctors prescribe physical therapy and physical therapy.
- Laser, magnetic, ultrasonic therapy;
- Electrophoresis;
- Massage;
- Therapeutic baths (mud, salt);
- Reflexology (acupuncture).
Physiotherapy is exclusively performed in a medical institution under the supervision of a doctor-physiotherapist. You control the degree of tension in the joints, the proper execution of the exercises.
Prevention of arthritis and arthrosis.
To protect the joints it is possible if you follow some simple rules:
- Load connections must be moderate. The excess of weight, frequency of training with heavy weights creates a threat to the connection of overload. In addition, the probability of damage increases many times.
- Proper, balanced nutrition. Daily diet must include all the information needed vitamins and minerals. With little food should take food additives, vitamins, minerals, complex.
- Women should leave the frequent and prolonged wearing high-heel shoes. Every inch heel increases the load on the spine by 10 kg of lap 20.
- Protect the joints of hypothermia. Arthritis, unlike osteoarthritis, is the result of the infection, the low temperature contributed to its dissemination in the body.
Conclusion.
Arthritis and osteoarthritis can be a serious problem in the life of an active person, regardless of age. Pain and stiffness in the limbs much reduced quality of life because of the disability, and the disability. It is important to understand what are the differences between the diseases in time to see a specialist – you spend the differential diagnosis, that is to say, for the treatment of arthritis and osteoarthritis.
































